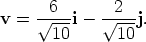in
both Cartesian and polar forms.
in
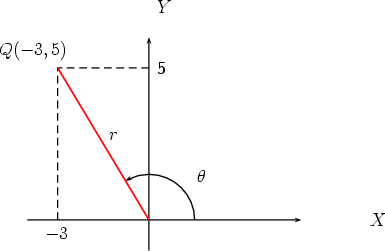
both Cartesian and polar forms. Find the polar coordinates of the point Q(-3, 5) and write down the vector  in
both Cartesian and polar forms.
in
both Cartesian and polar forms.
 ) are the
polar coordinates, then the Cartesian and polar forms of
) are the
polar coordinates, then the Cartesian and polar forms of  are xi + yj and
r cos
are xi + yj and
r cos  i + r sin
i + r sin 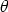 j respectively, where
j respectively, where

and
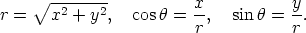
The Cartesian form is therefore 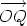 = -3i + 5j.
= -3i + 5j.
To find the polar form, first find r and 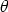 . We have
. We have
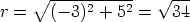
and
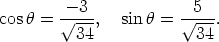
Note that  is in the second quadrant (x negative, y positive). Using the inverse
cosine function on a calculator, we obtain (in radians)
is in the second quadrant (x negative, y positive). Using the inverse
cosine function on a calculator, we obtain (in radians)
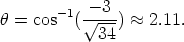
Hence the polar form of 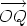 is
is 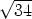 cos 2.11i +
cos 2.11i +  sin 2.11j
sin 2.11j
Find the Cartesian form of the vector 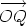 whose polar form is
whose polar form is
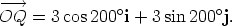

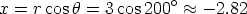
and
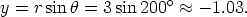
Therfore the Cartesian form of 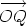 is -2.82i - 1.03j. Find the polar form of the
vector
is -2.82i - 1.03j. Find the polar form of the
vector 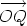 whose Cartesian form is
whose Cartesian form is
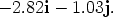
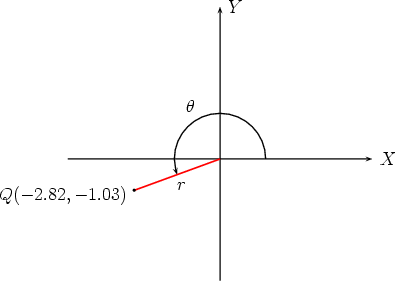
Notice that this is just the reverse of the previous problem, included here to illustrate
that care is needed to find the polar angle  , especially when it’s in the third quadrant.
, especially when it’s in the third quadrant.
First,
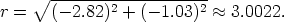
As cos 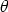 =
= 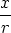 and sin
and sin 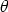 =
= 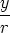 , we see that
, we see that

Note also that
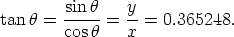
The difficulty with using a calculator to find 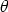 is that the inverse cosine function
returns values between 0 and
is that the inverse cosine function
returns values between 0 and  , while the inverse sine and inverse tan functions return
values between -
, while the inverse sine and inverse tan functions return
values between - /2 and
/2 and  /2. So to obtain a positive angle in the third quadrant, we
must make an adjustment to the calculator output. With the calculator in radian
mode, any one of the three formulas
/2. So to obtain a positive angle in the third quadrant, we
must make an adjustment to the calculator output. With the calculator in radian
mode, any one of the three formulas
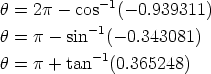
will give the right answer, which in radians is 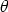 = 3.492 (or in degrees approximately
200°).
= 3.492 (or in degrees approximately
200°).
Find the vector v of magnitude 2 in the direction of the vector r = 3i - j.
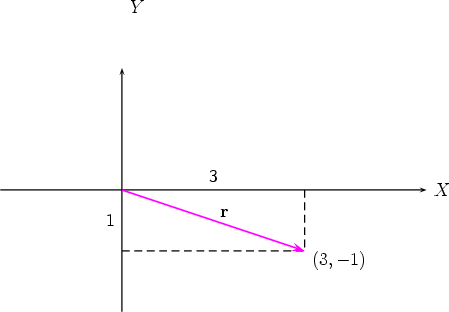
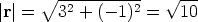
Therefore the unit vector 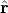 in the same direction as r is
in the same direction as r is
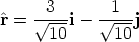
Multiplying  by 2 gives the required vector,
by 2 gives the required vector,